
你喜歡HTC手機的板面嗎?
下載HTC Home便可以在Windows Vista 或 Windows 7桌面上體驗HTC.
HTC Home 2是一個時鐘, 天氣預報和動畫的部件(widget). 你可以看雲漂浮在你的桌面上, 雨滴滑落在你的屏幕, 甚至雷擊.

除了HTC Home的風格之外, 它還提供Windows Phone 7的Metro風格.

http://www.htchome.org/
http://androidbiancheng.blogspot.com/





<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/captureimage"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Call for ACTION_IMAGE_CAPTURE"
/>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imagecaptured"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
</LinearLayout>
package com.AndroidImageCapture;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ImageView;
public class AndroidImageCapture extends Activity {
ImageView imageiewImageCaptured;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Button buttonImageCapture = (Button)findViewById(R.id.captureimage);
imageiewImageCaptured = (ImageView)findViewById(R.id.imagecaptured);
buttonImageCapture.setOnClickListener(buttonImageCaptureOnClickListener);
}
Button.OnClickListener buttonImageCaptureOnClickListener
= new Button.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Intent intent = new Intent(android.provider.MediaStore.ACTION_IMAGE_CAPTURE);
startActivityForResult(intent, 0);
}};
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
if (resultCode == RESULT_OK)
{
Bundle extras = data.getExtras();
Bitmap bmp = (Bitmap) extras.get("data");
imageiewImageCaptured.setImageBitmap(bmp);
}
}
}
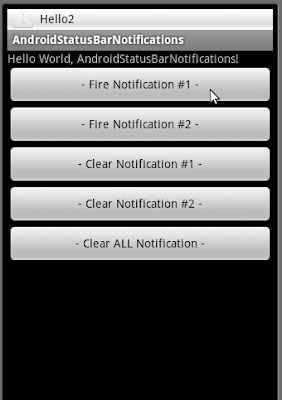
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/fire1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="- Fire Notification #1 -"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/fire2"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="- Fire Notification #2 -"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/clear1"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="- Clear Notification #1 -"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/clear2"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="- Clear Notification #2 -"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/clearall"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="- Clear ALL Notification -"
/>
</LinearLayout>
package com.AndroidStatusBarNotifications;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.Notification;
import android.app.NotificationManager;
import android.app.PendingIntent;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class AndroidStatusBarNotifications extends Activity {
private static final int ID_My_Notification_1 = 1;
private static final int ID_My_Notification_2 = 2;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Button buttonFire1 = (Button)findViewById(R.id.fire1);
Button buttonFire2 = (Button)findViewById(R.id.fire2);
Button buttonClear1 = (Button)findViewById(R.id.clear1);
Button buttonClear2 = (Button)findViewById(R.id.clear2);
Button buttonClearAll = (Button)findViewById(R.id.clearall);
buttonFire1.setOnClickListener(buttonFire1OnClickListener);
buttonFire2.setOnClickListener(buttonFire2OnClickListener);
buttonClear1.setOnClickListener(buttonClear1OnClickListener);
buttonClear2.setOnClickListener(buttonClear2OnClickListener);
buttonClearAll.setOnClickListener(buttonClearAllOnClickListener);
}
private Button.OnClickListener buttonClearAllOnClickListener
= new Button.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String ns = Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE;
NotificationManager mNotificationManager = (NotificationManager)getSystemService(ns);
mNotificationManager.cancelAll();
}};
private Button.OnClickListener buttonClear1OnClickListener
= new Button.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
clearNotification(ID_My_Notification_1);
}};
private Button.OnClickListener buttonClear2OnClickListener
= new Button.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
clearNotification(ID_My_Notification_2);
}};
private void clearNotification(int notification_id){
String ns = Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE;
NotificationManager mNotificationManager = (NotificationManager)getSystemService(ns);
mNotificationManager.cancel(notification_id);
}
private Button.OnClickListener buttonFire1OnClickListener
= new Button.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
fireNotification(ID_My_Notification_1);
}};
private Button.OnClickListener buttonFire2OnClickListener
= new Button.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
fireNotification(ID_My_Notification_2);
}};
private void fireNotification(int notification_id){
//Get a reference to the NotificationManager
String ns = Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE;
NotificationManager mNotificationManager = (NotificationManager)getSystemService(ns);
//Instantiate the Notification
int icon = android.R.drawable.ic_dialog_alert;
CharSequence tickerText = "Hello" + String.valueOf(notification_id);
long when = System.currentTimeMillis();
Notification notification = new Notification(icon, tickerText, when);
//Define the Notification's expanded message and Intent
Context context = getApplicationContext();
CharSequence contentTitle = "My Notification" + String.valueOf(notification_id);
CharSequence contentText = "Hello My Notification!" + String.valueOf(notification_id);
//Intent notificationIntent = new Intent(AndroidStatusBarNotifications.this, AndroidStatusBarNotifications.class);
Intent notificationIntent = new Intent(getBaseContext(), AndroidStatusBarNotifications.class);
PendingIntent contentIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(AndroidStatusBarNotifications.this, 0, notificationIntent, 0);
notification.setLatestEventInfo(context, contentTitle, contentText, contentIntent);
//Pass the Notification to the NotificationManager
mNotificationManager.notify(notification_id, notification);
}
}


<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/fire"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="- Fire Notification -"
/>
</LinearLayout>
package com.AndroidStatusBarNotifications;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.Notification;
import android.app.NotificationManager;
import android.app.PendingIntent;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class AndroidStatusBarNotifications extends Activity {
private static final int ID_My_Notification = 1;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Button buttonFire = (Button)findViewById(R.id.fire);
buttonFire.setOnClickListener(buttonFireOnClickListener);
}
private Button.OnClickListener buttonFireOnClickListener
= new Button.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//Get a reference to the NotificationManager
String ns = Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE;
NotificationManager mNotificationManager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(ns);
//Instantiate the Notification
int icon = android.R.drawable.ic_dialog_alert;
CharSequence tickerText = "Hello";
long when = System.currentTimeMillis();
Notification notification = new Notification(icon, tickerText, when);
//Define the Notification's expanded message and Intent
Context context = getApplicationContext();
CharSequence contentTitle = "My Notification";
CharSequence contentText = "Hello My Notification!";
//Intent notificationIntent = new Intent(AndroidStatusBarNotifications.this, AndroidStatusBarNotifications.class);
Intent notificationIntent = new Intent(getBaseContext(), AndroidStatusBarNotifications.class);
PendingIntent contentIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(AndroidStatusBarNotifications.this, 0, notificationIntent, 0);
notification.setLatestEventInfo(context, contentTitle, contentText, contentIntent);
//Pass the Notification to the NotificationManager
mNotificationManager.notify(ID_My_Notification, notification);
}};
}

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/start"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="- Start -"
/>
</LinearLayout>
package com.AndroidProgressDialog;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.ProgressDialog;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.SystemClock;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class AndroidProgressDialog extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Button buttonStart = (Button)findViewById(R.id.start);
buttonStart.setOnClickListener(new Button.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
new asyncTaskUpdateProgress().execute();
}
});
}
public class asyncTaskUpdateProgress extends AsyncTask<Void, Integer, Void> {
int progress;
ProgressDialog progressDialog;
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(Void result) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
progressDialog.dismiss();
}
@Override
protected void onPreExecute() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
progress = 0;
progressDialog = ProgressDialog.show(AndroidProgressDialog.this, "ProgressDialog", "Wait!");
}
@Override
protected Void doInBackground(Void... arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
while(progress<100){
progress++;
SystemClock.sleep(20);
}
return null;
}
}
}


<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.AndroidTakePicture"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0">
<application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<activity android:name=".AndroidTakePicture"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:screenOrientation="portrait"
>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="7" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA"></uses-permission>
</manifest>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/takebutton"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="- Take Picture -"
/>
<SurfaceView
android:id="@+id/previewsurface"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
</LinearLayout>
package com.AndroidTakePicture;
import java.io.IOException;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.graphics.PixelFormat;
import android.hardware.Camera;
import android.hardware.Camera.PictureCallback;
import android.hardware.Camera.ShutterCallback;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.SurfaceHolder;
import android.view.SurfaceView;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class AndroidTakePicture extends Activity implements SurfaceHolder.Callback{
Camera myCamera;
SurfaceView previewSurfaceView;
SurfaceHolder previewSurfaceHolder;
boolean previewing = false;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
getWindow().setFormat(PixelFormat.UNKNOWN);
previewSurfaceView = (SurfaceView)findViewById(R.id.previewsurface);
previewSurfaceHolder = previewSurfaceView.getHolder();
previewSurfaceHolder.addCallback(this);
previewSurfaceHolder.setType(SurfaceHolder.SURFACE_TYPE_PUSH_BUFFERS);
Button buttonTakePicture = (Button)findViewById(R.id.takebutton);
buttonTakePicture.setOnClickListener(new Button.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
myCamera.takePicture(shutterCallback, rawPictureCallback, jpegPictureCallback);
}});
}
ShutterCallback shutterCallback = new ShutterCallback(){
@Override
public void onShutter() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}};
PictureCallback rawPictureCallback = new PictureCallback(){
@Override
public void onPictureTaken(byte[] arg0, Camera arg1) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}};
PictureCallback jpegPictureCallback = new PictureCallback(){
@Override
public void onPictureTaken(byte[] arg0, Camera arg1) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Bitmap bitmapPicture = BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(arg0, 0, arg0.length);
}};
@Override
public void surfaceChanged(SurfaceHolder arg0, int arg1, int arg2, int arg3) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(previewing){
myCamera.stopPreview();
previewing = false;
}
try {
myCamera.setPreviewDisplay(arg0);
myCamera.startPreview();
previewing = true;
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
myCamera = Camera.open();
}
@Override
public void surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
myCamera.stopPreview();
myCamera.release();
myCamera = null;
previewing = false;
}
}

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.AndroidCameraPreview"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0">
<application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<activity android:name=".AndroidCameraPreview"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="7" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA"></uses-permission>
</manifest>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<SurfaceView
android:id="@+id/previewsurface"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
</LinearLayout>
package com.AndroidCameraPreview;
import java.io.IOException;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.PixelFormat;
import android.hardware.Camera;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.SurfaceHolder;
import android.view.SurfaceView;
public class AndroidCameraPreview extends Activity implements SurfaceHolder.Callback{
Camera myCamera;
SurfaceView previewSurfaceView;
SurfaceHolder previewSurfaceHolder;
boolean previewing = false;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
getWindow().setFormat(PixelFormat.UNKNOWN);
previewSurfaceView = (SurfaceView)findViewById(R.id.previewsurface);
previewSurfaceHolder = previewSurfaceView.getHolder();
previewSurfaceHolder.addCallback(this);
previewSurfaceHolder.setType(SurfaceHolder.SURFACE_TYPE_PUSH_BUFFERS);
}
@Override
public void surfaceChanged(SurfaceHolder arg0, int arg1, int arg2, int arg3) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(previewing){
myCamera.stopPreview();
previewing = false;
}
try {
myCamera.setPreviewDisplay(arg0);
myCamera.startPreview();
previewing = true;
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
myCamera = Camera.open();
}
@Override
public void surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
myCamera.stopPreview();
myCamera.release();
myCamera = null;
previewing = false;
}
}



package com.AndroidLog;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
public class AndroidLog extends Activity {
private static final String TAG = "AndroidLog";
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Log.i(TAG, "onCreate");
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDestroy();
Log.i(TAG, "onPause()");
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onPause();
Log.i(TAG, "onPause()");
}
@Override
protected void onRestart() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onRestart();
Log.i(TAG, "onRestart()");
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onResume();
Log.i(TAG, "onResume()");
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onStart();
Log.i(TAG, "onStart()");
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onStop();
Log.i(TAG, "onStop()");
}
}





<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<VideoView
android:id="@+id/video"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
</LinearLayout>
package com.AndroidVideoView;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.MediaController;
import android.widget.VideoView;
public class AndroidVideoView extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
VideoView videoView = (VideoView)findViewById(R.id.video);
String src = "rtsp://v2.cache2.c.youtube.com/CjYLENy73wIaLQm3JbT_9HqWohMYESARFEIJbXYtZ29vZ2xlSARSBXdhdGNoYIvJo6nmx9DvSww=/0/0/0/video.3gp";
videoView.setVideoURI(Uri.parse(src));
videoView.setMediaController(new MediaController(this));
videoView.requestFocus();
videoView.start();
}
}


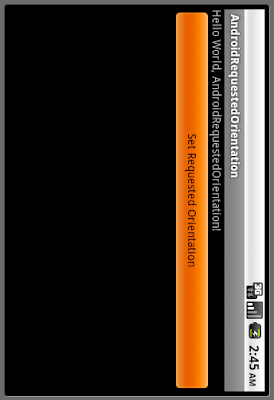
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/setrequestedorientation"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Set Requested Orientation"
/>
</LinearLayout>
package com.AndroidRequestedOrientation;
import android.app.ListActivity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.pm.ActivityInfo;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.ListView;
public class SetRequestedOrientationActivity extends ListActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setListAdapter(new ArrayAdapter<String>(this,
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, OrientationString));
getListView().setTextFilterEnabled(true);
}
static final String[] OrientationString = new String[] {
"SCREEN_ORIENTATION_UNSPECIFIED",
"SCREEN_ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE",
"SCREEN_ORIENTATION_PORTRAIT",
"SCREEN_ORIENTATION_USER",
"SCREEN_ORIENTATION_BEHIND",
"SCREEN_ORIENTATION_SENSOR",
"SCREEN_ORIENTATION_NOSENSOR"
};
static final int[] OrientationSetting = new int[] {
ActivityInfo.SCREEN_ORIENTATION_UNSPECIFIED,
ActivityInfo.SCREEN_ORIENTATION_LANDSCAPE,
ActivityInfo.SCREEN_ORIENTATION_PORTRAIT,
ActivityInfo.SCREEN_ORIENTATION_USER,
ActivityInfo.SCREEN_ORIENTATION_BEHIND,
ActivityInfo.SCREEN_ORIENTATION_SENSOR,
ActivityInfo.SCREEN_ORIENTATION_NOSENSOR
};
@Override
protected void onListItemClick(ListView l, View v, int position, long id) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onListItemClick(l, v, position, id);
Intent intent = new Intent();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putInt("setting", OrientationSetting[position]);
intent.putExtras(bundle);
setResult(RESULT_OK, intent);
finish();
}
}
package com.AndroidRequestedOrientation;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.pm.ActivityInfo;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class AndroidRequestedOrientation extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Button buttonSetRequestedOrientation = (Button)findViewById(R.id.setrequestedorientation);
buttonSetRequestedOrientation.setOnClickListener(new Button.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(AndroidRequestedOrientation.this,
SetRequestedOrientationActivity.class);
startActivityForResult(intent, 0);
}});
}
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
if (requestCode==0)
{
if(resultCode == RESULT_OK){
int OrientationSetting = data.getIntExtra("setting",
ActivityInfo.SCREEN_ORIENTATION_UNSPECIFIED);
setRequestedOrientation(OrientationSetting);
}
}
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.AndroidRequestedOrientation"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0">
<application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<activity android:name=".AndroidRequestedOrientation"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity android:name=".SetRequestedOrientationActivity"></activity>
</application>
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="4" />
</manifest>
<activity android:name=".MyActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:screenOrientation="portrait">




<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/input"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/write"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Write"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/read"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Read"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/output"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
</LinearLayout>
package com.AndroidInternalStorage;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class AndroidInternalStorage extends Activity {
String FILENAME = "MyFile";
EditText edittextInput;
TextView textviewOutput;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
edittextInput = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.input);
Button buttonWrite = (Button)findViewById(R.id.write);
Button buttonRead = (Button)findViewById(R.id.read);
textviewOutput = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.output);
buttonWrite.setOnClickListener(buttonWriteOnClickListener);
buttonRead.setOnClickListener(buttonReadOnClickListener);
}
private Button.OnClickListener buttonWriteOnClickListener
= new Button.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String string = edittextInput.getText().toString();
FileOutputStream fos;
try {
fos = openFileOutput(FILENAME, Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
fos.write(string.getBytes());
fos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}};
private Button.OnClickListener buttonReadOnClickListener
= new Button.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
FileInputStream fis;
try {
fis = openFileInput(FILENAME);
byte[] input = new byte[fis.available()];
while (fis.read(input) != -1) {}
textviewOutput.setText(new String(input));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}};
}
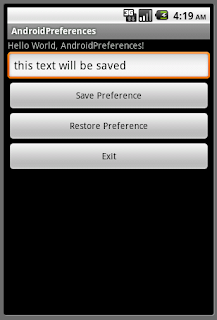
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/preferencestring"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/savepreference"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Save Preference"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/restorepreference"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Restore Preference"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/exit"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Exit"
/>
</LinearLayout>
package com.AndroidPreferences;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
public class AndroidPreferences extends Activity {
EditText myText;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
myText = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.preferencestring);
Button buttonSave = (Button)findViewById(R.id.savepreference);
Button buttonRestore = (Button)findViewById(R.id.restorepreference);
Button buttonExit = (Button)findViewById(R.id.exit);
buttonSave.setOnClickListener(buttonSaveOnClickListener);
buttonRestore.setOnClickListener(buttonRestoreOnClickListener);
buttonExit.setOnClickListener(buttonExitOnClickListener);
SharedPreferences myPreferences = getPreferences(0);
String myPreferencesString = myPreferences.getString("key", "default value");
myText.setText(myPreferencesString);
}
private Button.OnClickListener buttonSaveOnClickListener
= new Button.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
SharedPreferences settings = getPreferences(0);
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = settings.edit();
editor.putString("key", myText.getText().toString());
editor.commit();
}};
private Button.OnClickListener buttonRestoreOnClickListener
= new Button.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
SharedPreferences myPreferences = getPreferences(0);
String myPreferencesString = myPreferences.getString("key", "default value");
myText.setText(myPreferencesString);
}};
private Button.OnClickListener buttonExitOnClickListener
= new Button.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
finish();
}};
}


<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Very simple code to copy a picture from the application's resource into the external file"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/info"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
</LinearLayout>
package com.AndroidExternalFiles;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class AndroidExternalFiles extends Activity {
TextView textInfo;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
textInfo = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.info);
String state = Environment.getExternalStorageState();
if (Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED.equals(state)) {
createExternalStoragePrivateFile();
} else if (Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED_READ_ONLY.equals(state)) {
textInfo.setText("The media is Read Only!");
} else {
textInfo.setText("Something Wrong!");
}
}
void createExternalStoragePrivateFile() {
// Create a path where we will place our private file on external
// storage.
File file = new File(getExternalFilesDir(null), "myFile.jpg");
try {
// Very simple code to copy a picture from the application's
// resource into the external file.
InputStream is = getResources().openRawResource(R.drawable.icon);
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(file);
byte[] data = new byte[is.available()];
is.read(data);
os.write(data);
is.close();
os.close();
textInfo.setText("File have been wrote.");
} catch (IOException e) {
// Unable to create file, likely because external storage is
// not currently mounted.
textInfo.setText("IOException: " + e.toString());
}
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.AndroidExternalFiles"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0">
<application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<activity android:name=".AndroidExternalFiles"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
</manifest>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/info"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textx"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="X: "
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/texty"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Y: "
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textz"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Z: "
/>
</LinearLayout>
package com.AndroidOrientationInfo;
import java.util.List;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.hardware.Sensor;
import android.hardware.SensorEvent;
import android.hardware.SensorEventListener;
import android.hardware.SensorManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class AndroidOrientationInfo extends Activity {
SensorManager sensorManager;
boolean accelerometerPresent;
Sensor accelerometerSensor;
TextView textInfo, textX, textY, textZ;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
textInfo = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.info);
textX = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textx);
textY = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.texty);
textZ = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textz);
sensorManager = (SensorManager)getSystemService(Context.SENSOR_SERVICE);
List<Sensor> sensorList = sensorManager.getSensorList(Sensor.TYPE_ORIENTATION);
if(sensorList.size() > 0){
accelerometerPresent = true;
accelerometerSensor = sensorList.get(0);
String strSensor = "Name: " + accelerometerSensor.getName()
+ "\nVersion: " + String.valueOf(accelerometerSensor.getVersion())
+ "\nVendor: " + accelerometerSensor.getVendor()
+ "\nType: " + String.valueOf(accelerometerSensor.getType())
+ "\nMax: " + String.valueOf(accelerometerSensor.getMaximumRange())
+ "\nResolution: " + String.valueOf(accelerometerSensor.getResolution())
+ "\nPower: " + String.valueOf(accelerometerSensor.getPower())
+ "\nClass: " + accelerometerSensor.getClass().toString();
textInfo.setText(strSensor);
}
else{
accelerometerPresent = false;
}
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onResume();
if(accelerometerPresent){
sensorManager.registerListener(accelerometerListener, accelerometerSensor, SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_NORMAL);
Toast.makeText(this, "Register accelerometerListener", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onStop();
if(accelerometerPresent){
sensorManager.unregisterListener(accelerometerListener);
Toast.makeText(this, "Unregister accelerometerListener", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
private SensorEventListener accelerometerListener = new SensorEventListener(){
@Override
public void onAccuracyChanged(Sensor arg0, int arg1) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent event) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
textX.setText("X: " + String.valueOf(event.values[0]));
textY.setText("Y: " + String.valueOf(event.values[1]));
textZ.setText("Z: " + String.valueOf(event.values[2]));
}};
}

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/info"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textx"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="X: "
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/texty"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Y: "
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textz"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Z: "
/>
</LinearLayout>
package com.AndroidAccelerometer;
import java.util.List;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.hardware.Sensor;
import android.hardware.SensorEvent;
import android.hardware.SensorEventListener;
import android.hardware.SensorManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class AndroidAccelerometer extends Activity {
SensorManager sensorManager;
boolean accelerometerPresent;
Sensor accelerometerSensor;
TextView textInfo, textX, textY, textZ;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
textInfo = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.info);
textX = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textx);
textY = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.texty);
textZ = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textz);
sensorManager = (SensorManager)getSystemService(Context.SENSOR_SERVICE);
List<Sensor> sensorList = sensorManager.getSensorList(Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER);
if(sensorList.size() > 0){
accelerometerPresent = true;
accelerometerSensor = sensorList.get(0);
String strSensor = "Name: " + accelerometerSensor.getName()
+ "\nVersion: " + String.valueOf(accelerometerSensor.getVersion())
+ "\nVendor: " + accelerometerSensor.getVendor()
+ "\nType: " + String.valueOf(accelerometerSensor.getType())
+ "\nMax: " + String.valueOf(accelerometerSensor.getMaximumRange())
+ "\nResolution: " + String.valueOf(accelerometerSensor.getResolution())
+ "\nPower: " + String.valueOf(accelerometerSensor.getPower())
+ "\nClass: " + accelerometerSensor.getClass().toString();
textInfo.setText(strSensor);
}
else{
accelerometerPresent = false;
}
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onResume();
if(accelerometerPresent){
sensorManager.registerListener(accelerometerListener, accelerometerSensor, SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_NORMAL);
Toast.makeText(this, "Register accelerometerListener", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onStop();
if(accelerometerPresent){
sensorManager.unregisterListener(accelerometerListener);
Toast.makeText(this, "Unregister accelerometerListener", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
private SensorEventListener accelerometerListener = new SensorEventListener(){
@Override
public void onAccuracyChanged(Sensor arg0, int arg1) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent event) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
textX.setText("X: " + String.valueOf(event.values[0]));
textY.setText("Y: " + String.valueOf(event.values[1]));
textZ.setText("Z: " + String.valueOf(event.values[2]));
}};
}